Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is also known as Spastic colon, Irritable colon, functional bowel disease
Medical Definition of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a gastrointestinal disorder without any structural pathology, characterized by pain in the abdomen, and constipation and diarrhoea.
What Is Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)?
In normal English, this means abdominal (stomach area) pain and discomfort. There is no structural problem, ie the intestines look normal. The symptoms are stomach pain with constipation, diarrhoea or both, can alternate between the two.
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic, long-lasting, disorder in which the bowels do not work normally. It is a mechanical malfunction rather than tissue damage, unlike Crohn’s disease. The end result is stomach pain and constipation, diarrhoea, or constipation alternating with diarrhoea. About 10% of the population of North America are affected, twice as many women as men. Although the condition causes discomfort it does not cause tissue damage or increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
In general most suffers can manage their symptoms by managing diet, lifestyle and stress. A few will need medication and counselling.
Clinical Diagnosis of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)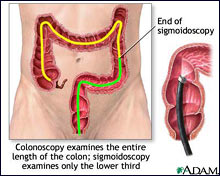
The clinical diagnosis is called The Rome II Criteria
- The patient should have 12 weeks of abdominal pain in the past 12 months.
- Pain is relieved by defecation (passing stools) or gas. The onset of disease (pain) is with a decrease in stool frequency and form.
- May be characterized as diarrhoea predominant or constipation-predominant, or may alternate between diarrhoea and constipation.
Signs and symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a group of symptoms—including abdominal pain and changes in bowel movements, but there is no tissue damage. As per the Rome II Criteria, the symptoms have to be for a long duration, at least 12 weeks. There are 4 classifications depending on bowel movement, ie diarrhoea or constipation. Diarrhoea is common (IBS-D), if constipation is common (IBS-C), both are common (IBS-M), or neither occurs very often (IBS-U).
Although IBS is not life-threatening it has a negative effect on the quality of life of the suffers, such as not wanting to go out, missing school or work.
Psychological issues are also associated with IBS such as anxiety, major depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome.
The symptoms may be different from person to person and can include:
- Transient (comes and goes) cramps or pain, like a spasm or colic, in the stomach area. Often relieved by the passing of gas or stools.
- Constipation — infrequent stools that may be hard and dry, can be long-lasting and painful.
- Feeling like you haven’t finished a bowel movement
- Diarrhoea — frequent loose stools
- Alternating between diarrhoea and constipation
- The urgency to go, which means they have to get to the toilet quickly. A morning rush is common.
- Mucus in the stools (mucus colitis).
- Swollen or bloated stomach area
- Abdominal bloating due to gas. This causes heartburn, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia and flatulence.
- Discomfort in the upper stomach area or feeling uncomfortably full or nauseous after eating a normal size meal
- Pain increases after a meal and due to stress and emotion.
- The pain subsides when asleep.
- Heartburn.
- Food intolerance
- Tiredness.
- Backache.
- Muscle pains.
- Women with IBS may have more symptoms during their menstrual periods.
- About a third of men and women who have IBS also report sexual dysfunction typically in the form of a reduction in libido.
Most Susceptible People
Women under the age of 45 are the most susceptible, with the abdominal pain increasing during menstruation.
Although it seems to run in families it has no genetic component. Family environment, ie same food, same environment, same habits etc. You are a product of your parents, with the same habits causing the same problems in both generations.
IBS is more common in women than men, almost twice as common. Although the symptoms can begin at any age, the most commonly begin in people in their 20s. Although anxiety and stress do not directly cause IBS they make the symptoms worse.
Have a mental health problem. Anxiety, depression, a personality disorder and a history of childhood sexual abuse are risk factors. For women, domestic abuse may be a risk factor as well.
Causes Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
The exact cause is according to modern medicine is unknown. Many theories are circulating, including, gut-brain axis problems, genetic factors, food sensitivity and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. It presents in a similar fashion to inflammatory bowel diseases, but these are ruled out as IBS has no tissue damage. It is purely a mechanical problem, caused by abnormal activity of the muscles of the intestines and/or the nerves that control the muscles. The abnormalities of the muscle cannot be seen under a microscope.
Recent research has shown the alterations in the intestinal microbiota (microbes in the gut), play a big role in the problem. More healthcare professionals, such as myself, are looking to fix the imbalance in the gut by adding healthy probiotics.
Diagnosis of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
There is no test for diagnosing IBS directly, all other diseases conditions have to be eliminated before IBS is diagnosed. So it is diagnosed by elimination if there is no other cause it has to be IBS.
Various procedures are used to eliminate other diseases such as Crohn’s
CT or ultrasound will be normal
Endoscopy can be used to eliminate the possibility of Crohn’s. It will be normal.
Patients with constipation can have a Sitz Marker study. This involves swallowing a pill containing x-ray markers so that the passage of the pill can be tracked. An x-ray is taken 5 days later. It is normal.
Stool samples are also taken and tested for parasites, ie worms etc, electrolyte present etc. Again they are normal.
As we have no idea what the ideal gut flora, (gut microbes), should be we cannot use this as a diagnostic tool.
Cure or Treatment (conventional) for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)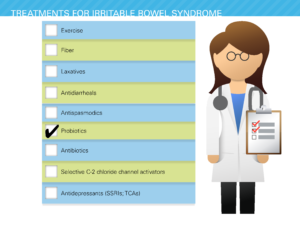
As far as modern medicine is concerned there is no cure, so they only treat the symptoms. This includes dietary changes, medication and counselling.
For dietary changes, the patient has to identify foods that aggravate the condition. An increase in soluble fibre, a gluten-free diet.
The medication would include treating the symptoms as they arose, eg diarrhoea take loperamide, constipation some laxative. Antidepressants have been used to reduce the pain and deal with the emotional effects.
List of drugs used in IBS for various abdominal disorders —
| Symptom | Drug | Dose |
|---|---|---|
| Diarrhoea | ||
| Loperamide | 4 mg when necessary up to the maximum as per the package insert | |
| Cholestyramine resin | 4g with meals 12g per day | |
| Constipation | ||
| Psyllium husk | 3–4g twice a day with meals, then adjust | |
| Methylcellulose | 2g twice a day with meals, then adjust | |
| Calcium polycarbophil | 1g one to four times a day | |
| Lactulose syrup | 10–20 g twice a day | |
| Polyethene glycol 3350 | 17g in 250mL water four times a day | |
| Lubiprostone (Amitiza) | 24mg twice a day | |
| Magnesium hydroxide | 30–60mL once a day | |
| Abdominal pain | ||
| Smooth muscle relaxant | one to four times a day before a meal | |
| Tricyclic antidepressants | Start 25–50mg at bedtime, then adjust | |
| Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors | Begin small dose, increase as needed |
IBS Treatment: Peppermint Oil
Peppermint oil has a strong relaxation effect on the smooth muscle of the gut. This has been used for IBS-D, to reduce the stomach motility.
IBS Treatment: Psychotherapy, biofeedback and hypnosis.
Stress aggravates IBS so reducing the stress by therapy or hypnosis will reduce the symptoms. Biofeedback is another technique to reduce stress by moderating their physical state.
IBS and Exercise
Moderate exercise is another potent stress reducer. The release of endorphins, similar chemical structure to morphine, reduces stress and pain. Exercise should always be part of your daily life. It has huge health benefits on all parts of your life.
IBS: Long-Term Prognosis
IBS is a long-term or chronic condition. It is marked by periods of greater symptoms (exacerbations) and lesser symptoms (remissions). Sometimes it is possible to uncover emotional or physical triggers for the exacerbations. If so, it may be possible to eliminate these triggers. In general, over time, the symptoms of IBS do not get worse nor do they progress to more serious conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) or cancer.
Effective Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Treatment of symptoms and not the cause is guaranteed not to solve the problem but prolong it.
The most effective treatment to date is the use of a live culture probiotics.
The probiotic has the following effects
- an anti-inflammatory effect, thus reducing the cramping and pain.
- assist in the digestion of food, preventing partial digestion and the formation of gasses
- because little gas is produced no bloating or flatulence
- normal stools are produced preventing both diarrhoea and constipation
Noster ProBiotics will greatly assist in the reduction of your IBS symptoms and will go a long way to providing you with a cure.
<
p style=”text-align: center;”>


